
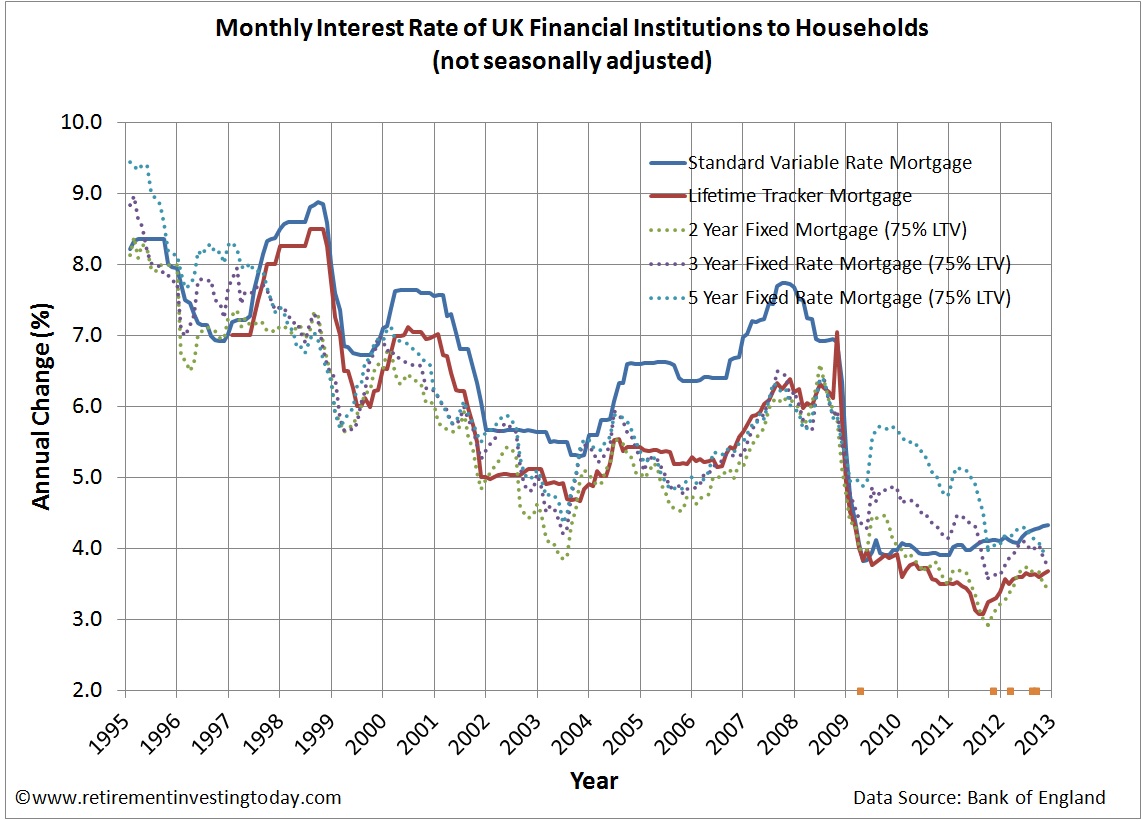
That’s because interest will be charged on top of your interest less often, giving interest less room to grow. Semi-annual compounding saves you money compared to monthly compounding. This means that while you might be making monthly mortgage payments, your mortgage interest will only be compounded twice a year. Mortgage interest in Canada is compounded semi-annually. You can use an APR calculator, or you can manually calculate your mortgage’s APR using the total interest paid, fees paid, and the loan term length. A mortgage’s APR reflects the true cost of borrowing for your mortgage. That’s why it can be a better idea to compare lenders based on their annual percentage rate (APR). Since you’ll need to pay these extra costs in order to borrow money, they can increase the actual cost of your mortgage.

Your mortgage might have other costs and fees, such as set-up fees or appraisal fees, that are necessary to get your mortgage. However, mortgage interest isn’t the only cost that you’ll need to pay. If you’re borrowing a larger amount of money, your mortgage payment may also be higher due to interest being charged on a larger principal balance. If you now have a higher mortgage rate, your mortgage payment will be higher to account for the higher interest charges. This can change your mortgage rate, which will impact the amount of mortgage interest due. This is why your mortgage payment amount can change when you renew your mortgage or refinance your mortgage. Your regular mortgage payment amount is set by your lender so that you’ll be able to pay off your mortgage on time based on your selected amortization period. This means that with every mortgage payment, you will be paying both your mortgage principal and your mortgage interest. The mortgage interest charged is included in your regular mortgage payments. For borrowers, mortgage interest is charged based on your mortgage principal balance. Interest is charged by lenders in exchange for allowing you to borrow money. A higher principal balance means that you’ll be paying more mortgage interest compared to a lower principal balance, assuming the mortgage interest rate is the same. The amount of interest that you pay will depend on your principal balance. As you make mortgage payments, your principal balance will decrease. Your mortgage principal balance is the amount that you still owe and will need to pay back. This means that when you get a mortgage and borrow $400,000, your mortgage principal will be $400,000.
You will only need to borrow $400,000 from a bank or mortgage lender in order to finance the purchase of the home. For example, perhaps you bought a home for $500,000 after closing costs and made a down payment of $100,000. When looking at mortgages, the mortgage principal is the amount of money that you owe and will need to pay back. Interest is then charged on the principal for a loan, while an investor might earn money based on the principal that they invested. If rates decrease, your mortgage will be paid off faster.Ī principal is the original amount of a loan or investment. This will cause your mortgage to be paid off slower than scheduled. This will reduce the amount of principal that is being paid.
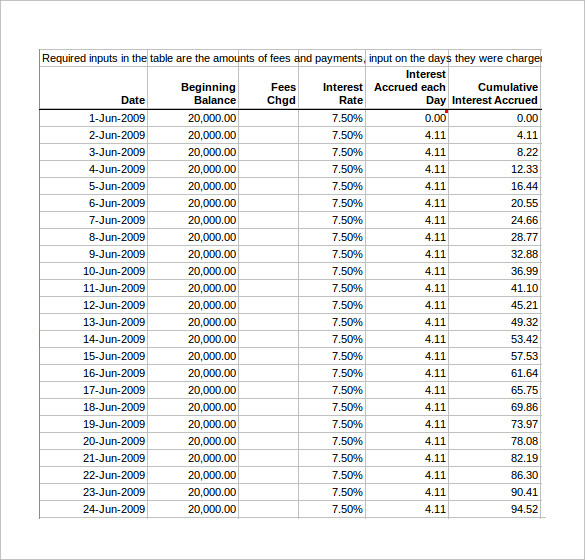
If interest rates rise, more of your mortgage payment will go towards interest.
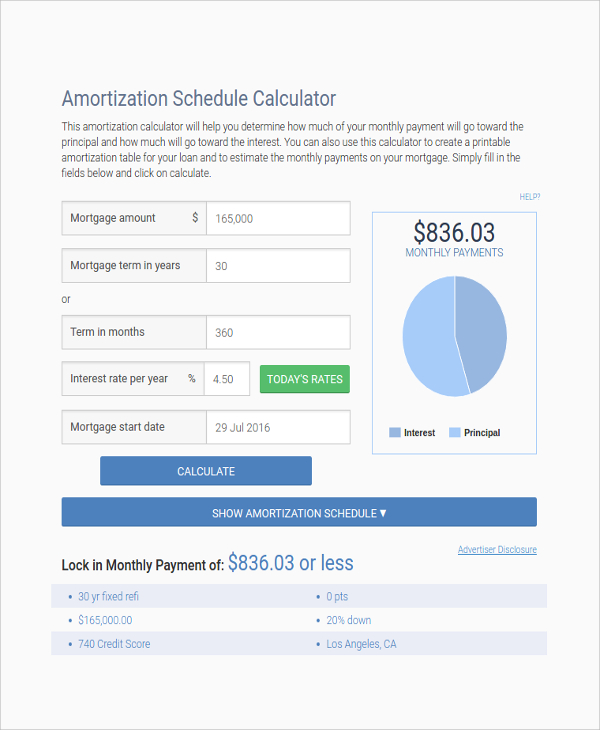
While the monthly mortgage payment for a variable-rate mortgage does not change, the portion going towards interest will change. On the other hand, variable-rate mortgages have a mortgage interest rate that can change. Your principal will be paid off at an increasingly faster rate as your term progresses. Fixed-rate mortgages have an interest rate that does not change. This behaviour can change depending on your mortgage type. This is why your initial monthly payment will have a larger proportion going towards interest compared to the interest payment near the end of your mortgage term. However, since your monthly mortgage payment stays the same, this means that the amount being paid towards your principal will become larger and larger over time. A smaller principal balance will result in less interest being charged. Your regular mortgage payments will stay the same for the entire length of your term, but the portions that go towards your principal balance or the interest will change over time.Īs your principal payments lower your principal balance, your mortgage will become smaller and smaller over time. When you make a mortgage payment, you are paying towards both your principal and interest.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
